In today’s digital-first world, a well-crafted website is more than just an online presence—it’s a vital tool for attracting customers, generating leads, and reinforcing brand identity. A thoughtfully designed site boosts visibility in search results and keeps users engaged through intuitive navigation, compelling visuals, and meaningful content.
This guide explores the entire web design process, breaking down each stage from early discovery and planning to launch and ongoing optimization. It reveals how designers and developers systematically turn ideas into functional, user-friendly digital experiences. Each phase—from defining goals and identifying target audiences to creating wireframes, integrating visuals, and conducting thorough quality checks—builds a strong foundation for the next, ensuring a cohesive and effective end product.
Today’s web development landscape also demands the integration of modern standards such as responsive design, accessibility compliance, and SEO best practices to stay competitive. While the journey from concept to deployment can seem complex, every step plays a crucial role in delivering a website that performs well, resonates with users, and supports long-term business goals.
In the sections that follow, we’ll walk through each phase of the web design process in detail, highlighting the strategies and decisions that shape a successful site. Whether you’re building from scratch or reimagining your existing platform, this roadmap will help ensure a smooth and strategic path to a high-impact online presence.
Key Takeaways
- A clear overview of the web design process sets strategic objectives and defines target audiences.
- Thorough planning and requirement gathering ensure robust timelines, resource allocation, and measurable goals.
- Detailed wireframing, SEO integration, and usability testing are crucial for creating an intuitive site architecture.
- Visual design must align with brand identity and incorporate responsive strategies to provide a seamless user experience.
- Building the website includes translating designs into code, integrating interactive elements, and rigorous cross-device testing.
- A smooth deployment, ongoing monitoring, regular maintenance, and iterative refinements are imperative for long-term success.
Overview of the Web Design Process Steps
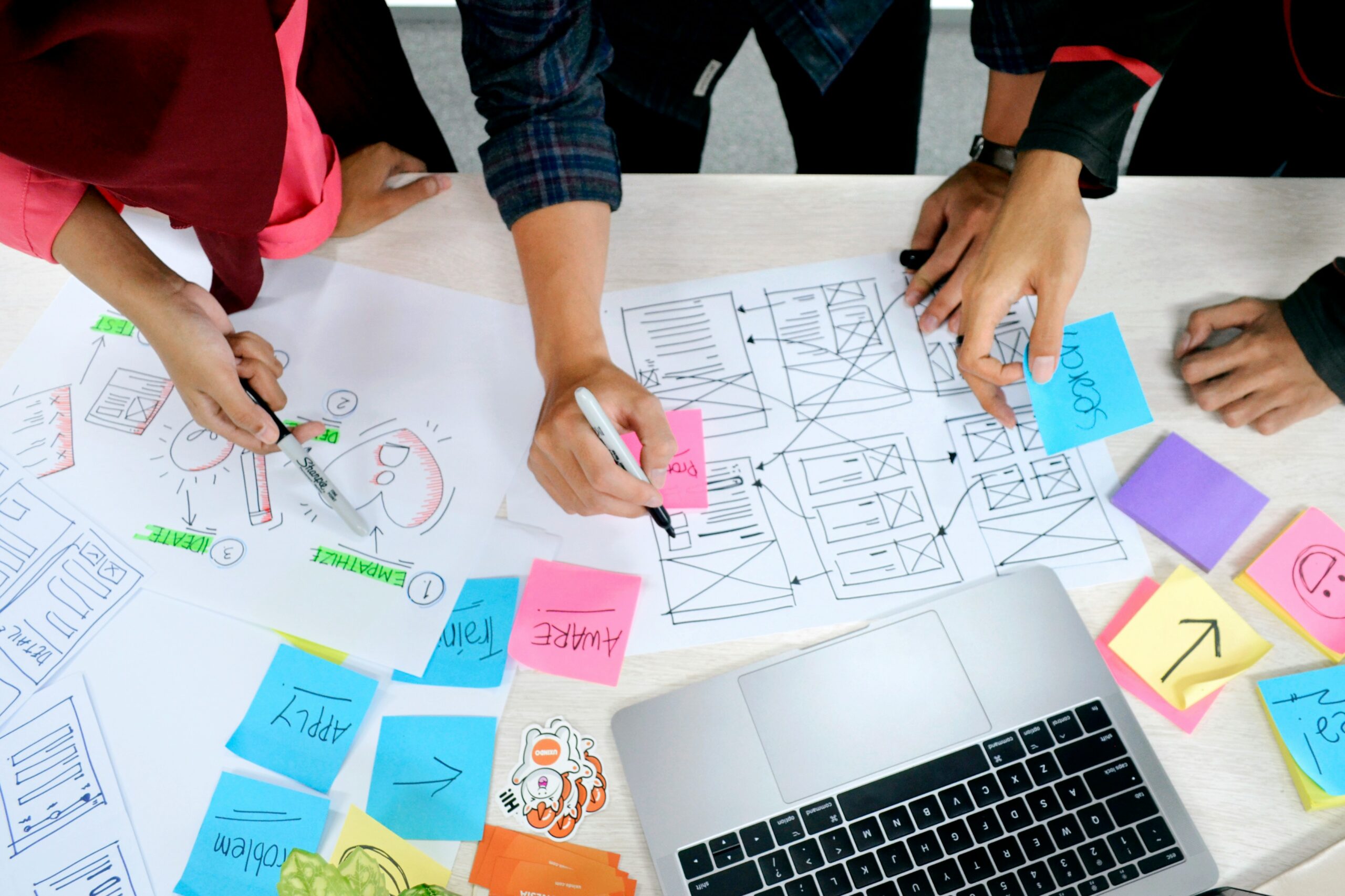

The overview of the web design process is a critical first step that sets the stage for all subsequent operations. At this stage, the project’s purpose, primary objectives, and the target audience are defined with precision. This initial step forces clarity in vision and helps align the digital strategy with the overall business goals. Defining project objectives means identifying what the website is intended to achieve—is it to generate leads, support e-commerce, or provide detailed information about services? It also includes a thorough analysis of user behavior and market research, crucial for anticipating user needs. For instance, when a web designer focuses on customer relationship management and content quality assurance, documenting these objectives in clear terms helps streamline the future workflow.
Defining Project Objectives and Target Audience
The first sub-step focuses on establishing measurable and realistic project objectives. Often, these include increasing site traffic through improved search engine visibility, enhancing user engagement through better interface design, and ensuring seamless navigation through intuitive layouts. Web designers analyze the intended audience’s behavior, preferences, and demographic data to curate a design that caters specifically to these users. With specific focus terms, the objectives also include enhanced usability testing results and higher conversion rates. The target audience might include professionals in diverse industries who expect an easy-to-navigate interface and a visually appealing layout that aligns with modern aesthetics.
Mapping Out All Design Phases and Requirements
Once objectives are clearly defined, the next step is mapping out all design phases. Every critical stage in this phase is documented, ensuring nothing is overlooked. From initial sketches and wireframes to integration of multimedia elements, each phase is planned with associated deadlines, responsibility assignments, and resource allocation. Requirements such as responsive design, SEO optimization, and adherence to accessibility standards are noted. A robust checklist that includes quality assurance markers ensures that every phase is executed with precision. For instance, incorporating key elements such as the proper use of HTML, CSS, and JavaScript is essential for smooth functionality as determined by modern web development practices.
Summarizing Key Deliverables at Each Stage
Finally, an effective summary of expected deliverables at each stage is imperative. This includes finalized wireframes, functional prototypes, documented design mockups, and test results from usability trials. Each deliverable should be aligned with predetermined goals and measurable outcomes. This structured approach not only minimizes scope creep but also ensures that any potential issues are addressed promptly. A table can effectively summarize these deliverables, listing design phase, expected outcomes, tools required, and deadlines. For example, during the design phase, deliverables might include color scheme selections and typography tests that align with the brand’s identity. Overall, this initial overview plays a pivotal role in setting clear expectations and communicating a unified vision to all stakeholders.
Planning and Gathering Requirements
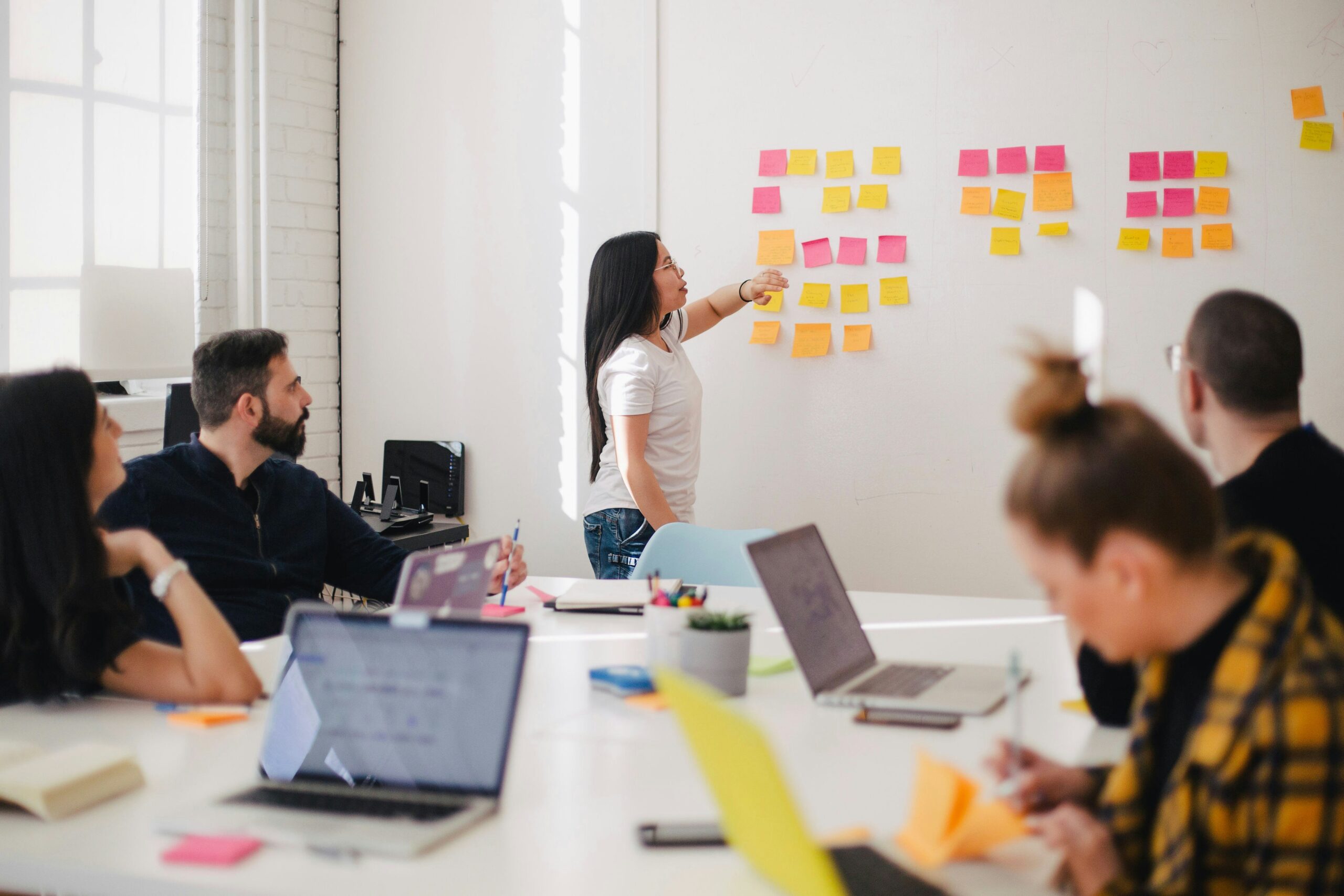

Effective planning and gathering of requirements form the backbone of a successful web design project. This stage is where strategic planning meets granular execution, ensuring that every element—from budget allocations to resource planning—is meticulously organized. When organizations invest in planning, they avoid common pitfalls such as scope creep, miscommunication among team members, and unforeseen technical challenges. Thorough planning also underpins the overall digital marketing strategy by connecting user interface design with advertising and market research insights, ensuring that the final website is designed to address both user behaviors and business needs.
Analyzing Business and User Needs
The first subheading under this section involves examining both business and user needs to create a design that is functional and intuitive. Analysis might involve surveys, focus groups, and usability studies to understand users’ expectations. For businesses, this step ensures that the design process is tightly aligned with marketing strategies and revenue goals, such as enhanced conversion rates and improved customer retention.
Creating a Project Timeline and Resource Plan
After understanding the requirements, the next crucial task is to create a detailed project timeline and resource plan. This plan outlines the sequence of tasks, deadlines, and critical milestones that ensure the project remains on schedule. The timeline should consider design, development, testing, and QA phases in a logical order, linking each phase with subsequent delivery targets. Allocating resources effectively requires identifying roles—such as those for web designers, content strategists, SEO specialists, and quality assurance testers—and ensuring that each team member understands their responsibilities. A well-structured timeline minimizes delays and overlaps and facilitates smooth transitions between phases. In practice, when managing projects with complex requirements such as responsive web design and multi-device compatibility, detailed timelines serve as the roadmap toward achieving project success.
Outlining Budget Allocation and Stakeholder Roles
Next, outlining the budget allocation and clearly defining stakeholder roles are essential for controlled project management. A well-considered budget ensures that every element—from high-quality graphic design and imagery to advanced tools for drag-and-drop functionality—is adequately funded. Clear roles for each stakeholder help foster accountability and prevent overlapping responsibilities. This stage typically involves meetings with business owners, project managers, and digital marketing teams to discuss detailed cost estimates. Key budget factors may include technology stack investments (like using WordPress or custom HTML/CSS solutions), licensing fees for design tools such as Adobe Photoshop, and costs related to hiring external digital marketing consultants. Documenting these allocations prevents unforeseen expenditures and maintains financial discipline.
Setting Measurable Goals for Design Success
Finally, establishing measurable goals is the culmination of the planning phase. These goals include specific performance indicators such as increased traffic, lower bounce rates, improved search engine rankings, and enhanced user engagement metrics. By incorporating tools such as Google Analytics and setting benchmarks for key engagement metrics, businesses can quantify the success of the design process. Setting clear, measurable goals ensures that every decision—whether it’s about typography, layout, or multimedia integration—directly contributes to the overall strategy. For example, setting a goal of reducing page load time by 20% or increasing user session duration by 15% provides actionable targets for each phase. This structured planning and explicit goal setting lead to a coherent and successful web design that aligns with any business’s strategic vision and operational capacity.
Structuring Information and Wireframe Development
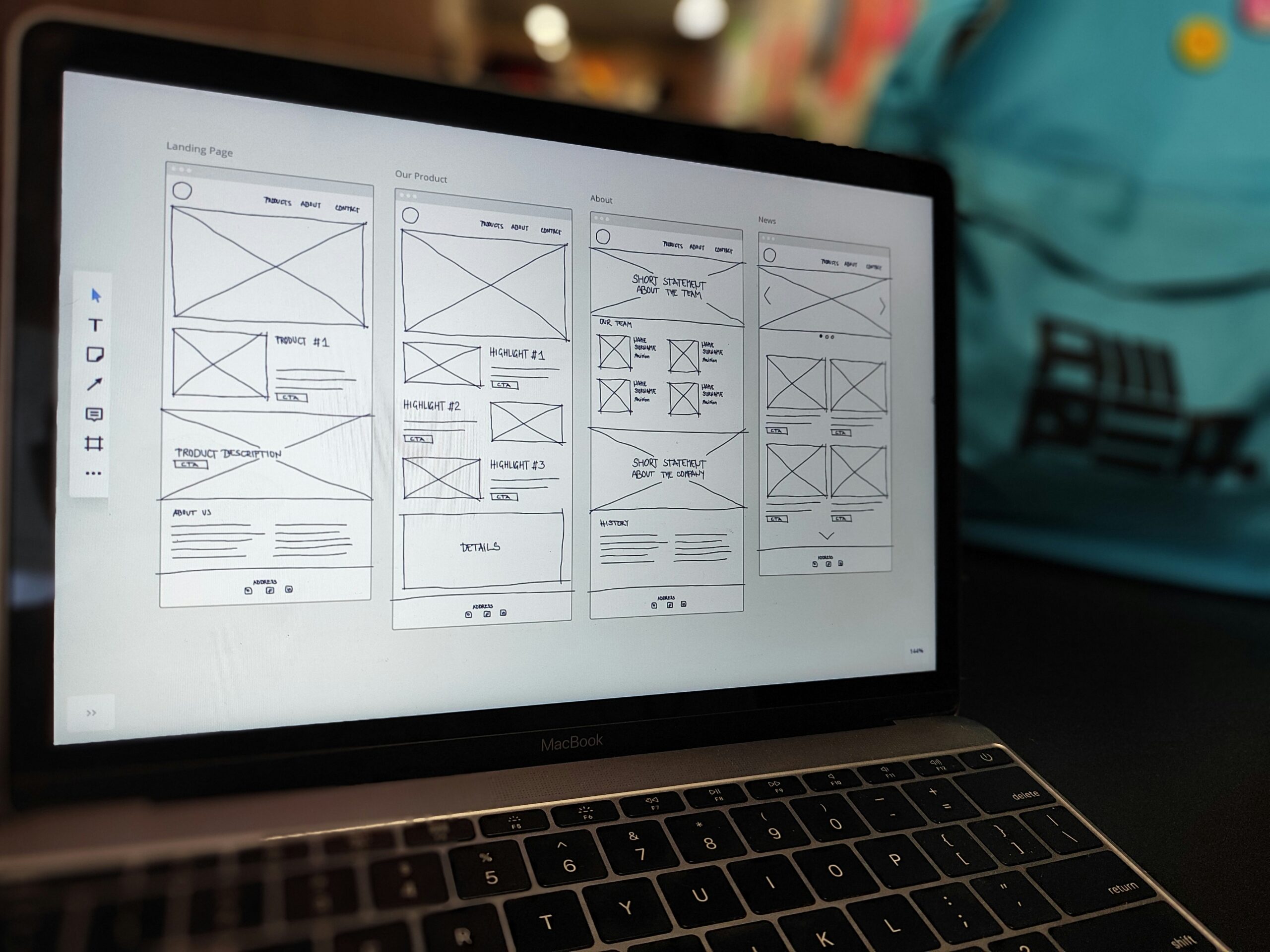
Structuring information and developing wireframes represent the bridge between conceptual planning and detailed design execution. At this stage, web designers focus on organizing content into a logical structure that facilitates easy navigation and enhances user experience. By creating comprehensive site architectures and user flows, designers ensure that users can intuitively locate key information such as digital marketing details, client workflows, and content management systems. This step is crucial because a well-structured website not only supports a seamless user experience but also plays a pivotal role in search engine optimization by improving the website’s crawlability and indexation rates.
Organizing Site Architecture and User Flow
The initial step in this phase is to organize the site architecture with a focus on clear navigational paths and user flows. A well-defined architecture ensures that users can effortlessly move from one section to another—a critical factor when managing complex websites that incorporate elements like graphic design portfolios, web application interfaces, and interactive elements. By modeling the user journey, designers can predict and address potential areas of friction, such as confusing buttons or hidden menu links. This demonstrates that investing time in planning the site flow not only enriches user experience but also bolsters business outcomes through improved engagement and conversion rates.
Sketching Wireframes and Defining Layout Grids
After establishing a clear site map and user flow, the next essential task is to sketch detailed wireframes. Wireframing involves creating simplified representations of the web page layout, which include key elements such as content sections, functional buttons, imagery placements, and call-to-action areas. Defining layout grids ensures that the design remains consistent and visually balanced across different pages and devices. Wireframes serve as blueprints for the final design, with each element—from spacing and alignment to multimedia integration—planned in meticulous detail. This stage often incorporates feedback from stakeholders, ensuring that the wireframe reflects both business priorities and user expectations. During this process, designers also consider responsive design strategies that accommodate various screen sizes, ensuring a coherent visual experience whether on a laptop, tablet, or mobile device.
Integrating SEO Fundamentals Into Structure
A crucial component during the wireframing stage is the integration of SEO fundamentals into the website structure. Modern search engine algorithms value well-organized, logically structured content that is easily accessible to crawlers. Including strategic placements of keywords such as “web design,” “information architecture,” and “content strategy” within layout grids can enhance the site’s visibility in search engine results. SEO integration does not only involve keyword placement but also involves technical elements like meta tags, header hierarchy, and optimized alt text for images. By embedding these strategies early in the design phase, websites can benefit from improved organic traffic, reducing the need for costly post-launch SEO overhauls.
Testing Usability With Initial Prototypes
Before moving on to full-scale development, testing usability with initial prototypes is paramount. Early testing with clickable wireframes or low-fidelity prototypes allows designers to gather real user feedback on navigation, layout, and functional elements. Usability testing identifies potential issues—such as misaligned buttons or confusing user flows—before significant resources are invested in development. Iterative user testing sessions help refine the design over multiple cycles, ensuring that problematic areas are corrected and the overall user experience is optimized. Evidence suggests that iterative testing can improve overall user satisfaction. Ultimately, thorough testing during this phase minimizes post-launch adjustments and contributes to a more seamless digital experience for end users.
Crafting Visual Design and Content Integration
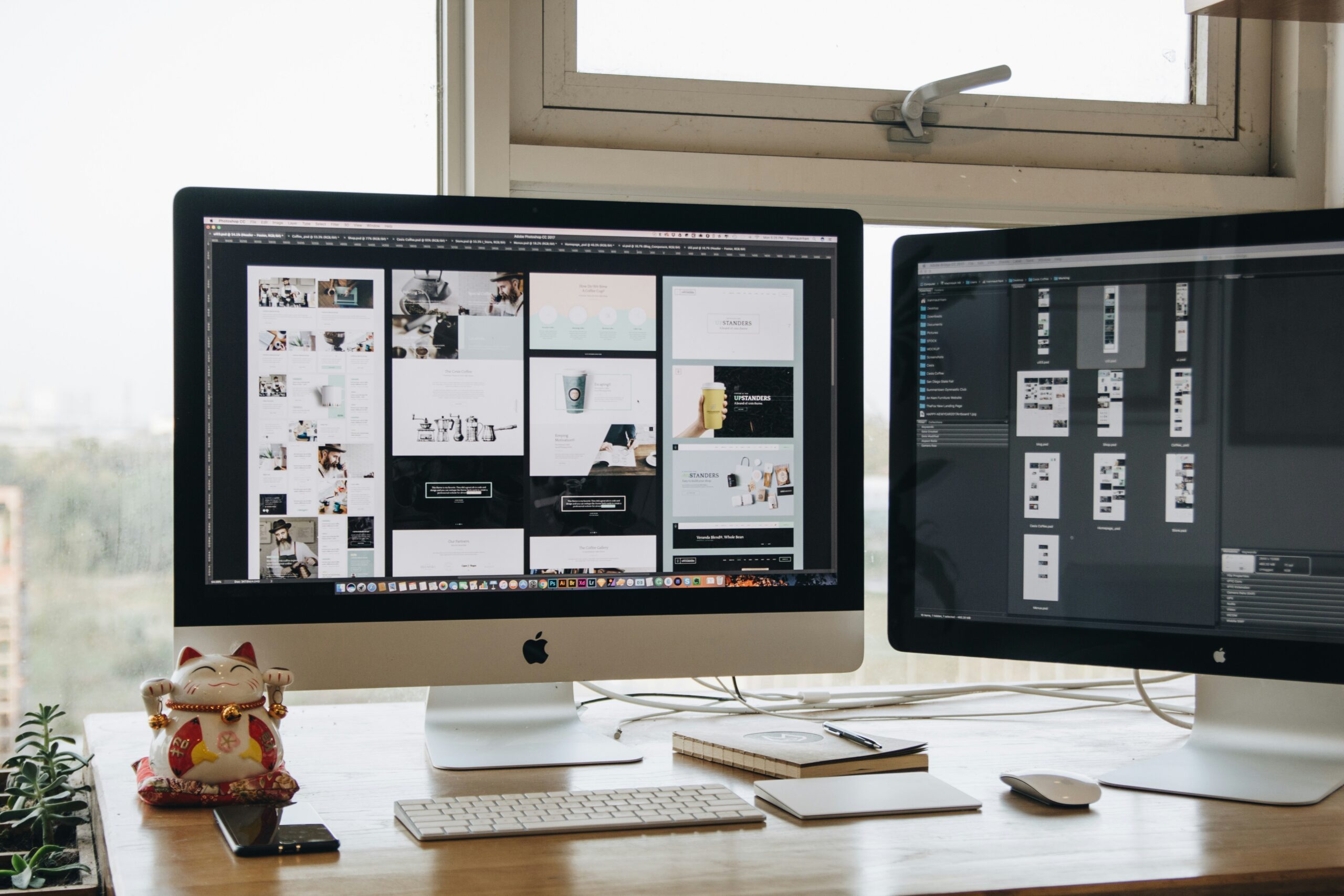

Crafting visual design and integrating creative content represent the phase where a website begins to take on its final form. Visual design goes beyond aesthetics; it encompasses the overall look, feel, and user experience of the website. By aligning color schemes, typography, imagery, and multimedia elements with a brand’s identity, designers create cohesive digital experiences that resonate with users. At this stage, the focus shifts towards both artistry and functionality, ensuring that while the site is visually appealing, it also supports usability and seamless navigation. For instance, whether the design incorporates HTML elements, responsive grids, or interactive plugins, every visual element must support the overall digital marketing and content strategy objectives.
Selecting Color Schemes and Typography
The process begins with the thoughtful selection of color schemes and typography. Colors evoke moods and signal brand personality—vibrant hues might be chosen for energetic brands, while subdued tones can imply reliability and professionalism. Typography selections complement this visual language; choosing fonts that are not only aesthetically pleasing but also legible on various devices is key, particularly when dealing with complex information architectures. Studies have shown that the right combination of colors and fonts can improve user interaction by over 30%. In practice, web designers balance brand guidelines with modern design trends to create a digital environment that is both attractive and effective.
Aligning Imagery and Visual Elements With Brand Identity
Subsequently, aligning imagery and visual elements with the brand identity helps consolidate the overall message being portrayed online. High-quality images, icons, and graphics are selected to reinforce key messages about a company’s products or services. For example, a business emphasizing cutting-edge technology might utilize clean, minimalist visuals and futuristic fonts. Visual consistency across pages builds a sense of cohesion and trust, which is essential for quality assurance and increased sales. By ensuring that imagery is optimized not only for aesthetics but also for fast loading times, designers contribute to both user experience and technical performance. Moreover, integrating custom icons and branded imagery can help differentiate a business in competitive marketplaces.
Incorporating Responsive Design Strategies
With user behavior increasingly shifting toward mobile devices, incorporating responsive design strategies is no longer optional but critical. Responsive design ensures that layouts, images, and interactive elements adjust fluidly to different screen sizes and resolutions, preserving functionality and visual appeal. This method not only improves accessibility but also meets the standards set by search engines that favor mobile-friendly websites. In the prototyping stage, mockups are tested across various devices to ensure seamless integration. Detailed guidelines for responsive layouts typically cover how menus collapse, how images resize, and how text reflows. Implementing these strategies leads to enhanced user experiences and stronger digital marketing outcomes.
Merging Text and Multimedia Effectively
The final step in this phase is merging text and multimedia elements in a cohesive manner. This involves careful content placement where text supports visuals rather than competing with them, and video or interactive elements complement the written content. Consistency in tone, style, and format across multimedia content is essential for effective communication. The use of infographics and embedded videos alongside text can boost understanding and retention by more than 40%, according to recent findings in media studies. The integration process also involves ensuring that multimedia elements are optimized for different devices, load quickly, and are accessible to all users—focusing on both design aesthetics and technical performance. In summary, crafting a visually engaging design while effectively integrating textual and multimedia content is critical to creating a website that is visually appealing, user-friendly, and well-optimized for search engines.
Building the Website and Quality Assurance
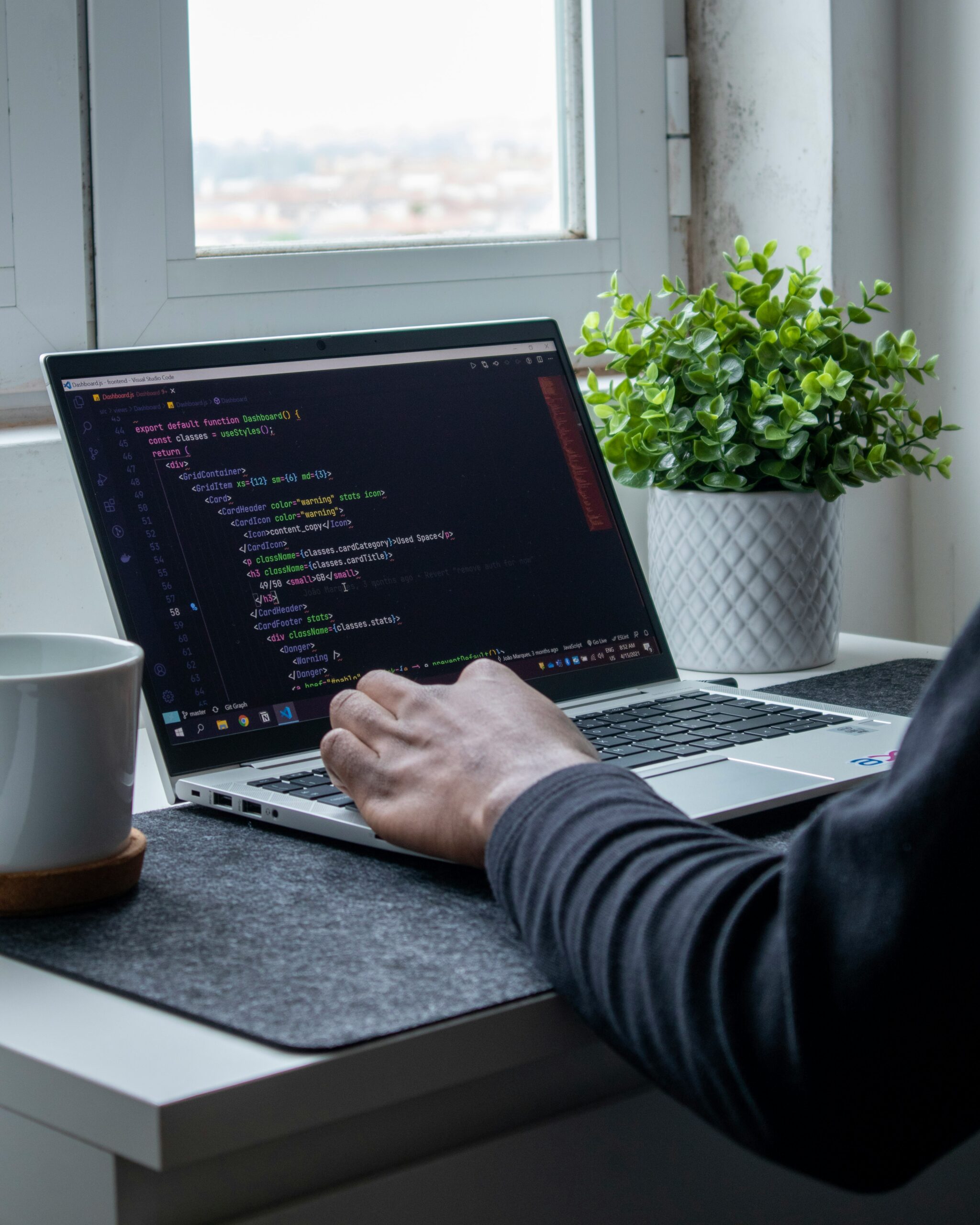

Once visual design and content integration reach completion, the next stage of web design involves translating these designs into a fully functional website. Building the website is where creative vision meets technical execution, and quality assurance ensures that every element performs as intended. This stage combines the technical expertise of web developers with ongoing testing efforts to deliver a seamless experience across various devices and browsers. Rigorous quality assurance procedures help detect and resolve issues related to functionality, responsiveness, and accessibility, ensuring that the website meets both business goals and user expectations.
Translating Designs Into Functional Code
The first sub-step in this stage is converting visual mockups and prototypes into robust, functional code. Web developers utilize programming languages such as HTML, CSS, and JavaScript to build the website’s front end, ensuring that every design element is accurately represented. During this phase, developers pay close attention to detail—from properly implementing layout grids to ensuring that navigation buttons and interactive elements function correctly. Utilizing frameworks like Bootstrap or custom solutions allows for faster development while maintaining a high level of quality assurance. This process also involves the integration of content management systems (CMS) that facilitate ongoing content updates without needing to alter the codebase significantly.
Integrating Interactive Elements and Plugins
Next, interactive elements and plugins are integrated to enhance user experience and drive engagement. Whether adding drag-and-drop functionality, interactive forms for client feedback, or marketing automation tools that connect to platforms like HubSpot, these elements are critical for creating dynamic web experiences. Plugins can provide additional capabilities—such as digital marketing analytics, advanced image sliders, or secure payment gateways—without requiring extensive custom code. These integrations must be tested rigorously to ensure that they work seamlessly with the website’s overall structure. As proven by studies in web usability (Krug, 2014), even minor interactive elements, when designed and implemented correctly, can increase engagement and improve overall site usability.
Conducting Rigorous Cross-Device Testing
After the website is built, rigorous cross-device testing is necessary to ensure that the website maintains consistent functionality and visual integrity across various devices, browsers, and screen sizes. Developers and quality assurance teams conduct thorough tests on desktops, laptops, tablets, and smartphones. This is crucial given the prevalence of mobile browsing; websites that perform poorly on mobile devices risk losing a significant portion of potential traffic. Tools such as BrowserStack and Google’s Lighthouse are employed to evaluate performance, page load times, and responsiveness. Testing also includes checking compatibility with different operating systems, ensuring that clients experience no disruption no matter what device they use.
Verifying Accessibility and Performance Standards
Finally, verifying accessibility and performance standards is an essential step in quality assurance. Accessibility audits ensure that the website meets international guidelines (such as the WCAG), making it usable for all users, including those with disabilities. This involves testing for proper use of ARIA labels, keyboard navigability, and sufficient color contrast. In addition to accessibility, performance metrics such as page speed, loading times, and SEO compliance are thoroughly measured. By addressing these issues during the quality assurance phase, developers ensure that the website not only functions correctly but also ranks well in search engines due to factors like fast load speeds and mobile optimization. Overall, this stage transforms an intricately designed concept into a reliable and high-performing website that meets both user expectations and business objectives.
Launch and Ongoing Improvement Strategies
After a website has been successfully built and tested, the launch phase marks the culmination of months of hard work. However, the launch itself is only a starting point; continuous improvement ensures that the website remains competitive, up-to-date, and aligned with user behavior and evolving market trends. During this final phase, businesses deploy systematic strategies to release the website without disruptions and implement mechanisms to gather user feedback, monitor analytics, and plan for iterative improvements over time.
Implementing a Smooth Deployment Strategy
A smooth deployment strategy is fundamental to successfully launching a website. This involves scheduling the launch during low-traffic periods, performing final backups, and ensuring that all stakeholders are informed of the transition. A well-executed deployment plan reduces the risk of issues such as downtime, performance lags, or data loss. Technical teams often use version control systems like Git to manage code changes and ensure that any critical issues can be rapidly addressed. A comprehensive launch checklist might include final testing results, confirmation that all interactive elements are working as intended, and a robust rollback plan in case of emergencies. By leveraging industry best practices and coordinating all aspects of the launch, businesses can minimize disruptions and ensure a seamless go-live experience.
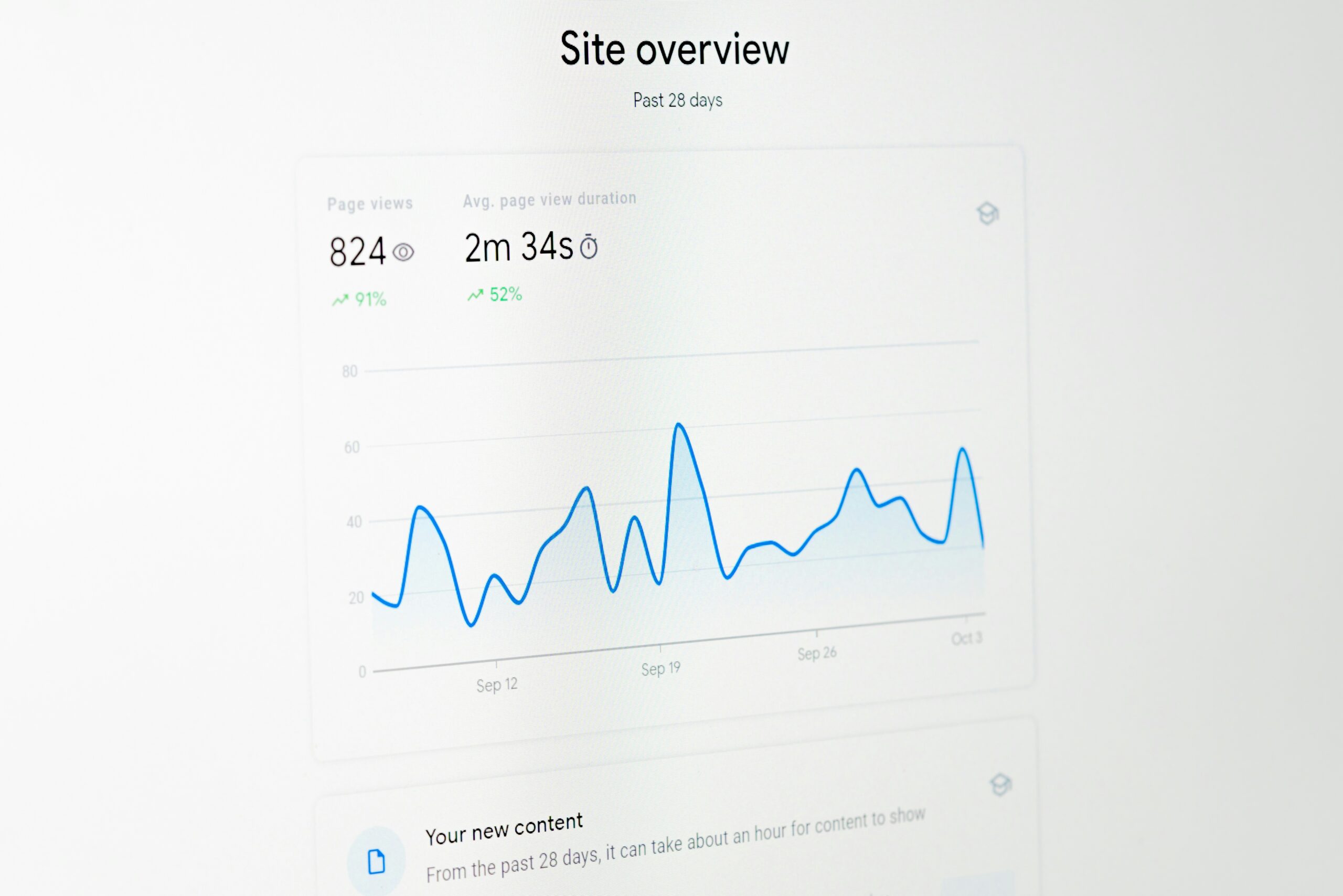
Monitoring Analytics and User Interactions
Immediately following deployment, monitoring real-time analytics and user interactions becomes essential. Businesses utilize tools such as Google Analytics to track page views, bounce rates, and conversion metrics, allowing them to gauge the initial reception of the website. User behavior insights—such as click-through trends or session duration—provide valuable feedback that highlights areas for potential improvement. Detailed monitoring helps identify any unexpected issues that may have slipped through the pre-launch testing phase. For example, if users report that certain buttons are not responsive on mobile devices, developers can quickly address these concerns. This constant flow of data ensures the business remains agile, adjusting content and functionality to meet emerging user needs.
Establishing Regular Maintenance Routines
Regular maintenance routines are critical for ensuring that the website continues to perform optimally long after launch. Scheduled updates for plugins, security patches, and periodic performance audits form the backbone of ongoing website management. These routines help prevent vulnerabilities, reduce downtime, and keep the website fresh with updated content and design elements. Maintenance not only involves technical updates but also revisiting content strategy to ensure that as market conditions and SEO guidelines evolve, the website remains compliant and competitive. Businesses might schedule monthly or quarterly reviews to assess site performance, integrating user feedback and monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs). This proactive approach safeguards long-term digital assets and reinforces user trust, ultimately contributing to sustained traffic growth and lead generation.
Iterating Based on Feedback and Performance Data
The iterative improvement process is a continuous cycle that leverages user feedback and performance data to refine the website over time. Effective iterations involve analyzing both qualitative user input and quantitative data from analytics tools. Based on this data, developers and designers can make incremental adjustments that enhance the user interface, improve usability, and boost communication of key value propositions. Iterative processes might involve A/B testing for different design elements, further optimizing the website’s layout, color schemes, or content presentation based on real-world performance. Peer-reviewed research and case studies have shown that iterative design improvements can increase conversion rates significantly—sometimes by over 20%—by ensuring the website evolves in line with user expectations. In summary, the launch is only the beginning of a dynamic, evolving process aimed at sustaining and improving the website’s performance over time.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How important is identifying the target audience in the web design process? A: Identifying the target audience is crucial as it informs the design’s functional and aesthetic choices. It ensures that the website aligns with user behavior and meets their needs, leading to a higher engagement rate and better conversion performance.
Q: What are the key benefits of integrating SEO fundamentals during wireframe development? A: Integrating SEO fundamentals early ensures the structure is easily crawlable by search engines and enhances overall site visibility. This includes optimal placement of keywords, proper header hierarchy, and the use of meta tags, which all contribute to improved search rankings.
Q: Why is responsive design a critical consideration during the visual design phase? A: Responsive design guarantees that the website adapts to various devices and screen sizes, providing a consistent and accessible experience. It improves usability, reduces bounce rates, and is favored by search engines, thereby increasing organic traffic.
Q: How can regular maintenance routines influence a website’s long-term performance? A: Regular maintenance ensures that the website remains up-to-date with security patches, updated plugins, and fresh content. This also addresses potential vulnerabilities and improves user experience, which is essential for sustained traffic and conversion rates.
Q: What role does user feedback play in the iterative improvement process? A: User feedback is a cornerstone for iterative improvements. By analyzing both qualitative and quantitative data, designers can make targeted refinements, enhancing usability, functionality, and overall user satisfaction, ultimately boosting the site’s performance.
Final Thoughts
The comprehensive web design process is a multifaceted journey that requires careful planning, creative execution, and continuous optimization. By following each step meticulously—from initial planning through to launch and ongoing improvements—businesses can ensure that their websites not only look attractive but also perform strategically to meet their digital marketing goals. This guide provides actionable insights and structured methodologies that help demystify the process while emphasizing the importance of quality assurance and user-focused design. As the digital landscape continues to evolve, the ability to manage, iterate, and enhance your web presence remains key to sustained success in an increasingly competitive market.