A technical SEO audit is a deep dive into a website’s technical infrastructure designed to ensure optimal performance, improve organic rankings, and boost overall visibility in search engines. This comprehensive guide explains the core principles, practical steps, and ongoing maintenance required to keep a website in top shape for both search engine crawlers and users.
Understanding the Core Principles of a Technical SEO Audit

Defining a Technical SEO Audit and Its Purpose
A technical SEO audit systematically evaluates a website’s technical elements to identify issues that can impede search engine performance. Its purpose is to enhance crawlability, fix indexing problems, and ensure adherence to SEO best practices dictated by search engine algorithms. For example, fixing broken links, improving site speed, and optimizing meta tags can increase organic traffic and conversion rates.
Key Factors Influencing Website SEO Performance
Several factors affect website SEO performance, including site architecture, URL structure, internal linking, page load speed, and mobile responsiveness. These factors work together to determine how effectively search engine bots can crawl and index a site. Additional elements like canonicalization, schema markup, and proper use of robots.txt files are critical for managing duplicate content and ensuring the best pages are served to users.
Essential Tools for Conducting a Comprehensive Technical SEO Audit
A robust audit requires specialized tools. Tools such as Screaming Frog, Sitebulb, Google Search Console, and SEMrush provide insights into crawl errors, duplicate content, and on-page issues while tracking key metrics like bounce rate and load time. These tools allow web developers and SEO specialists to quickly diagnose issues and measure improvements.
Differentiating Technical SEO From on-Page and Off-Page SEO
Technical SEO focuses on the website’s backend structure and performance, whereas on-page SEO concentrates on optimizing individual pages (through content, title tags, and meta descriptions) and off-page SEO involves external factors like backlinks and social signals. Technical SEO creates a robust framework that supports on-page efforts and ensures search engines can access all site areas.
The Significance of Regular Technical SEO Audits for Site Health
Regular audits are essential for maintaining a website’s health because sites continuously evolve. New pages, updates, and technical changes can introduce errors that hinder performance. Frequent audits help identify and resolve issues before they affect rankings, preserving traffic quality and enabling growth in competitive landscapes.
Executing a Step-by-Step Technical SEO Audit Guide

Initiating the Audit by Crawling Your Website
Begin with a comprehensive crawl using a reliable audit tool like Screaming Frog or Sitebulb. This process highlights issues such as broken links, missing tags, or duplicate content and provides a baseline for further analysis. Recording metrics like response codes (200, 404, etc.) and page load speeds helps identify immediate technical hurdles.
Reviewing Your XML Sitemap for Accuracy and Completeness
A well-structured XML sitemap is vital to ensure that search engines can discover and index all key pages. The audit should verify that the sitemap is accurate, up-to-date, and submitted to major search engines via Search Console. Outdated URLs or misconfigured entries can lead to drops in visibility.
Ensuring Only One Version of Your Site Is Browsable
It is important to configure your website so that only one version (with or without “www”, HTTP or HTTPS) is accessible to avoid duplicate content issues. Implementing 301 redirects from non-preferred to preferred versions consolidates ranking signals within a single URL structure, benefiting overall performance.
Performing Manual Google Searches to Assess Visibility
Complement automated tools with manual Google searches using queries like site:domain.com. This verifies that important pages are indexed and that no unwanted or duplicate pages appear in SERPs. Manual searches can reveal insights that some automation might miss.
Analyzing Your Site Architecture and URL Structure
A clear site architecture and logical URL structure enhance user experience and streamline search engine crawling. Hierarchical navigation, breadcrumb trails, and organized folder structures help both users and bots understand content relationships, directly influencing indexing efficiency and page relevance.
Optimizing Crawlability and Indexability for Search Engines
Checking and Refining Your Robots.txt File
The robots.txt file directs search engine bots on which pages or sections should not be crawled. It is crucial to confirm that this file blocks sensitive directories while allowing search engines to crawl valuable public content. Incorrect configurations might block essential pages and harm rankings.
Identifying and Resolving Indexation Issues
Indexation issues occur when pages that should appear in search results are missing from the index, or when unnecessary pages are included. Tools like Google Search Console help identify pages affected by noindex tags, duplicate content, or crawl errors. Fix these challenges by adjusting meta directives or using canonical tags to consolidate similar pages.
Managing Internal and External Links Effectively
Effective internal linking promotes a healthy site structure and distributes page authority among relevant pages. Audits need to ensure that internal links create a logical network that enhances navigation and user experience. Monitoring external links is also important to avoid passing link equity to low-quality or broken links.
Addressing Broken Links and Implementing Proper Redirects
Broken links frustrate users and reduce crawl efficiency by wasting search engine resources. A thorough audit should identify 404 errors and other broken links and then implement 301 redirects or update the links. Proper redirection preserves link equity and guides users seamlessly to the correct content.
Optimizing Crawl Budget for Efficient Search Engine Indexing
Crawl budget refers to the number of pages a search engine bot will crawl on your site in a given timeframe. Optimizing your crawl budget involves eliminating duplicate or low-value pages, improving internal linking, and ensuring fast server response times. This allows search engines to focus on your most valuable pages.
Enhancing Site Speed and Mobile Responsiveness

Testing and Improving Your Website’s Loading Speed
Website speed is a critical ranking factor that directly affects user experience and conversion rates. Measure load times using tools like Google PageSpeed Insights, GTmetrix, or Lighthouse. Strategies such as optimizing images, utilizing browser caching, and reducing server response times can significantly improve load times.
Evaluating and Optimizing Core Web Vitals
Core Web Vitals—Largest Contentful Paint (LCP), First Input Delay (FID), and Cumulative Layout Shift (CLS)—measure the user experience. Optimizing these metrics often involves code minification, server enhancements, and resource prioritization. Better core web vitals lead to improved page speed and interactivity.
Ensuring Your Website Is Mobile-Friendly and Responsive
Since many users access websites via mobile devices, a mobile-friendly design is essential. Responsive design, fluid grids, and adaptive images accommodate various screen sizes and enhance usability. Mobile optimization also prevents penalties from search engines that favor mobile-friendly sites.
Implementing Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) Where Appropriate
Accelerated Mobile Pages (AMP) provide a streamlined version of webpages that load quickly on mobile devices. Using AMP, where appropriate, can boost page speed and improve user retention, though it is important to maintain consistent branding and functionality with the main website.
Compressing Images and Minifying Code for Faster Load Times
Optimizing front-end performance involves compressing images without sacrificing quality and minifying CSS, JavaScript, and HTML files. These actions reduce latency and improve overall load times, ensuring a smoother experience for users and better performance in search rankings.
Addressing on-Page Technical Elements and Code Issues
Conducting on-Page Technical SEO Checks for Clear Hierarchy
On-page checks ensure that content hierarchy is clearly defined using appropriate heading tags (H1, H2, H3, etc.), bullet points, and internal links. A well-structured page helps search engines understand content and guides users to find the information they need quickly.
Implementing and Validating Schema Markup and Structured Data
Schema markup provides additional context about your content to search engines. Applying markup for articles, products, reviews, and events can enhance search results with rich snippets. Always validate structured data with tools like Google’s Structured Data Testing Tool to ensure accuracy.
Spotting and Fixing Common Code Problems
Code issues such as broken scripts, missing meta tags, or improper HTML element usage can negatively impact site performance. Use validation services like the W3C Validator to identify and fix these issues, improving both accessibility and crawlability.
Verifying Proper Use of Canonical Tags
Canonical tags indicate the preferred version of a page, preventing duplicate content issues and consolidating ranking signals for similar pages. Correct implementation ensures that search engines attribute the proper authority to each page.
Checking Hreflang Attributes for International Websites
For sites targeting multiple regions and languages, hreflang attributes are essential. They specify which version of a page should be shown to users based on their language and region, reducing duplicate content issues and ensuring relevant results in international search queries.
Leveraging Analytics and Maintaining Ongoing Site Performance
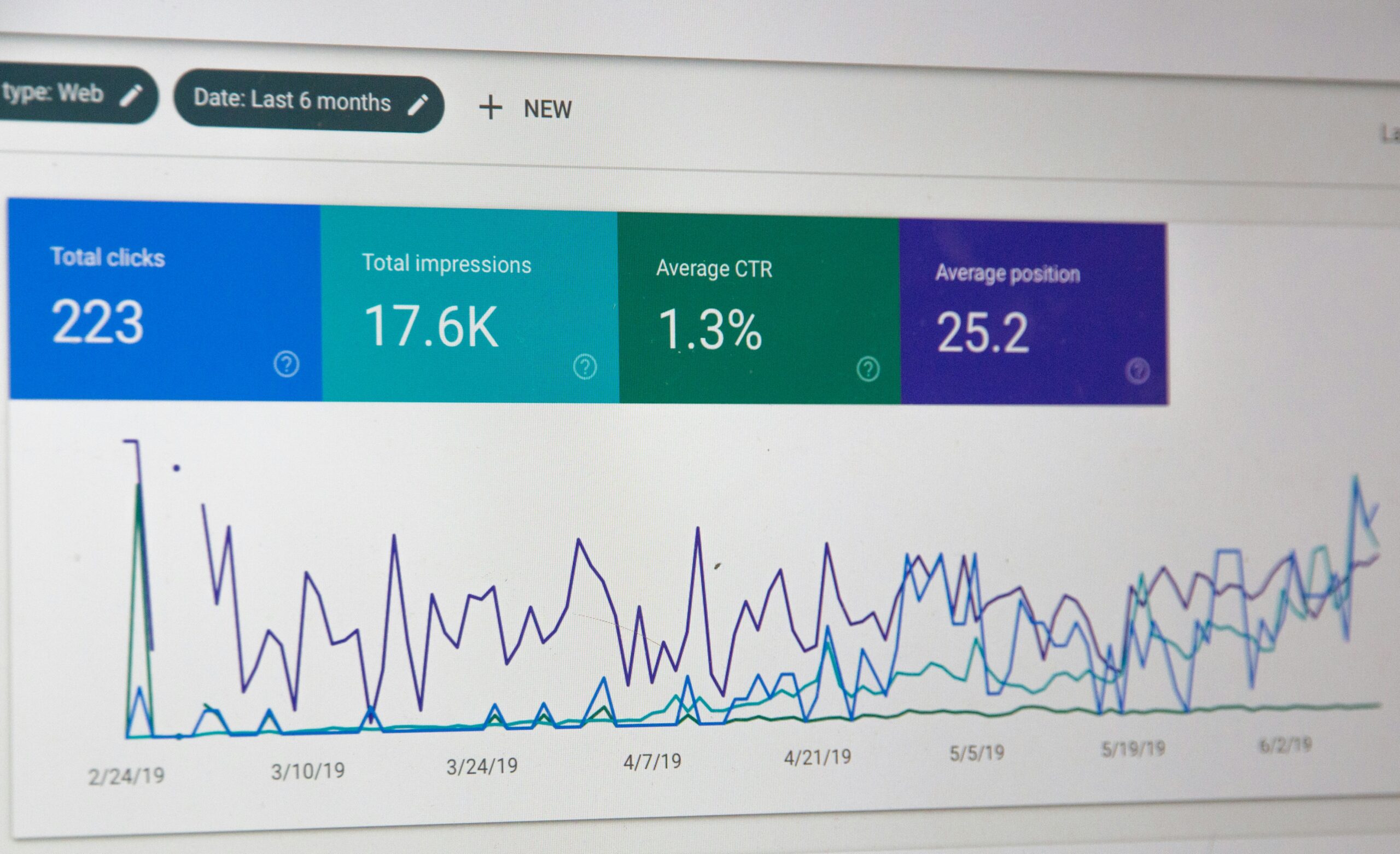
Utilizing Google Analytics and Search Console for Insights
Google Analytics and Search Console are vital for monitoring website performance and identifying potential issues. They provide important insights into user behavior, indexing status, click-through rates, and other key metrics, enabling data-driven SEO decisions.
Monitoring Key Site Metrics and Comparing Performance Over Time
Regularly track metrics such as organic traffic, bounce rate, conversions, and session duration to gauge SEO success. Comparing performance over time helps assess the impact of changes and supports ongoing strategic adjustments.
Identifying and Fixing Duplicate Content Issues
Duplicate content can confuse search engines and dilute ranking potential. Use available tools to identify duplicate content issues and address them through canonical tags, redirects, or content consolidation to ensure a unified ranking signal.
Ensuring Website Security With HTTPS
HTTPS is a critical ranking factor that also protects user data. Transitioning to HTTPS not only boosts SEO but also builds trust with users. Regularly update security certificates and resolve mixed content issues to maintain a secure browsing environment.
Keeping Abreast of Evolving SEO Best Practices and Algorithm Updates
SEO is a dynamic field with continuously evolving algorithms. Stay updated with industry news and search engine guidelines through training sessions, webinars, and authoritative SEO blogs. Ongoing learning helps adjust strategies and maintain a competitive edge.
Supplementary Visuals and Comparative Analysis
The following table summarizes key technical SEO elements, the attributes each addresses, and their benefits:
Final Thoughts
Technical SEO audits form the backbone of a website’s performance and digital competitiveness. By understanding core technical elements and undertaking systematic reviews, businesses can ensure their websites are accessible, fast, and easy for search engines to understand. This guide has outlined the essential steps from crawling the site and analyzing XML sitemaps to optimizing mobile performance and resolving code issues that collectively fortify a website’s technical foundation. Regular audits supported by robust analytics not only identify issues but also serve as a roadmap for sustainable growth. Ultimately, mastering technical SEO empowers businesses to adapt to evolving algorithms and consistently improve online visibility, driving increased traffic, leads, and revenue.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What is the main objective of a technical SEO audit?
A: The main objective is to identify and resolve technical issues that negatively affect a website’s visibility, ensuring efficient crawling, indexing, and optimal performance for both search engines and users.
Q: How frequently should a technical SEO audit be performed?
A: Audits should ideally be conducted quarterly or after major website changes to promptly address emerging technical issues.
Q: Which tools are most effective for performing a technical SEO audit?
A: Tools such as Screaming Frog, Google Search Console, SEMrush, and Sitebulb are commonly used to diagnose errors, monitor metrics, and validate SEO improvements.
Q: How do Core Web Vitals impact SEO performance?
A: Core Web Vitals measure crucial aspects of user experience like load speed and interactivity. Improving these metrics benefits user satisfaction and positively influences search rankings.
Q: What are canonical tags, and why are they important?
A: Canonical tags signal the preferred version of a page to search engines, reducing duplicate content issues and consolidating ranking signals for improved SEO performance.
Q: Can a poorly configured robots.txt file affect my site’s rankings?
A: Yes, an incorrectly set up robots.txt file can block essential pages from being crawled, leading to significant drops in indexation and organic traffic.
Q: How important is mobile responsiveness in technical SEO?
A: Mobile responsiveness is critical because most users access websites via mobile devices; a responsive design enhances user experience and is favored by search engine algorithms.
Q: What role does schema markup play in a technical SEO audit?
A: Schema markup provides contextual information to search engines, enabling enhanced search results such as rich snippets, which can improve click-through rates and overall visibility.
Q: Is HTTPS implementation necessary for a good SEO performance?
A: Yes, HTTPS is a confirmed ranking factor that not only boosts SEO but also improves website security and builds user trust.
Q: How does optimizing a site’s crawl budget benefit SEO efforts?
A: By improving crawl efficiency, valuable pages receive increased attention from search engine bots, ensuring faster indexing and improved ranking potential.